Control norovirus outbreaks
Hygiena International ATP test systems (involving a hand-held SystemSURE luminometer and UltraSnap swabs) have been used to evaluate the effectiveness of cleaning procedures, following two norovirus outbreaks on a cruise ship.
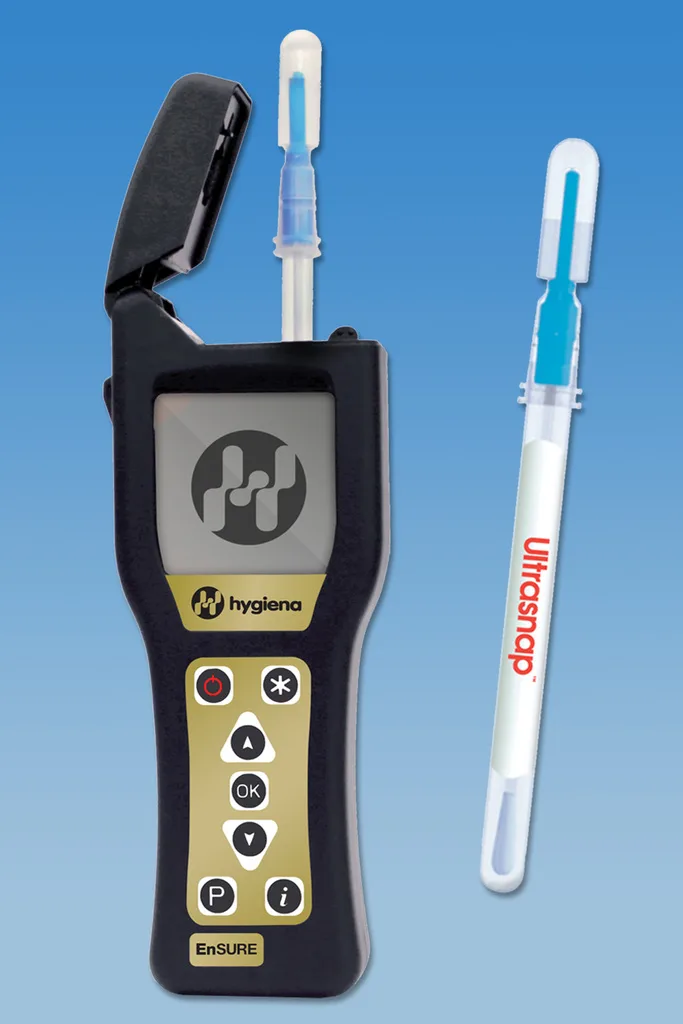
Any cleaning procedure is designed to remove residues of food and body fluids which contain large amounts of ATP i.e. adenosine triphosphate (the universal energy carrier). Residues of ATP remaining on surfaces after cleaning provide a direct, objective measure of the efficacy of the cleaning process and residual contamination risk.
The Hygiena UltraSnap swabs contain a reagent known as luciferase/luciferin in the bulb of the swab. Once the swab is snapped and the bulb squeezed, an oxidation reaction takes place with any ATP present, emitting light. The light produced is directly proportional to the amount of ATP in the area tested. This is a rapid method showing a strong correlation between ATP and microbial cells. Results measured in relative light units (RLU) can be obtained within 15 seconds.
The Hygiena SystemSURE test procedure is swift, provides a PASS/CAUTION/FAIL result and can be undertaken by personnel after only minimal training.
HSM publishes a weekly eNewsletter, delivering a carefully chosen selection of the latest stories straight to your inbox.
Subscribe here


